15.4 寫一個簡單的網頁應用
下邊的程序在端口8088上啓動了一個網頁服務器;SimpleServer會處理/test1url使它在瀏覽器輸出hello world。FormServer會處理'/test2url:如果url最初由瀏覽器請求,那麼它就是一個GET請求,並且返回一個form常量,包含了簡單的input表單,這個表單裏有一個文本框和一個提交按鈕。當在文本框輸入一些東西並點擊提交按鈕的時候,會發起一個POST請求。FormServer中的代碼用到了switch來區分兩種情況。在POST情況下,使用request.FormValue("inp")通過文本框的name屬性inp來獲取內容,並寫回瀏覽器頁面。在控制檯啓動程序並在瀏覽器中打開urlhttp://localhost:8088/text2`來測試這個程序:
示例 15.10 simple_webserver.go
package main
import (
"io"
"net/http"
)
const form = `
<html><body>
<form action="#" method="post" name="bar">
<input type="text" name="in" />
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>
</form>
</body></html>
`
/* handle a simple get request */
func SimpleServer(w http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
io.WriteString(w, "<h1>hello, world</h1>")
}
func FormServer(w http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/html")
switch request.Method {
case "GET":
/* display the form to the user */
io.WriteString(w, form)
case "POST":
/* handle the form data, note that ParseForm must
be called before we can extract form data */
//request.ParseForm();
//io.WriteString(w, request.Form["in"][0])
io.WriteString(w, request.FormValue("in"))
}
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/test1", SimpleServer)
http.HandleFunc("/test2", FormServer)
if err := http.ListenAndServe(":8088", nil); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
注:當使用字符串常量表示html文本的時候,包含<html><body></body></html>對於讓瀏覽器識別它收到了一個html非常重要。
更安全的做法是在處理器中使用w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/html")在寫入返回之前將header的content-type設置爲text/html
content-type會讓瀏覽器認爲它可以使用函數http.DetectContentType([]byte(form))來處理收到的數據
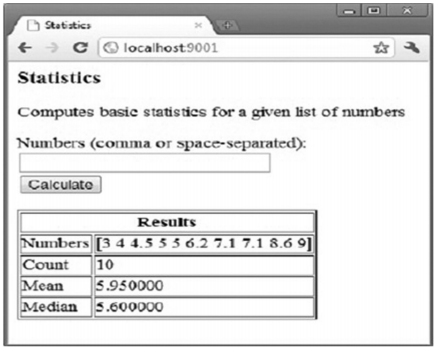
練習 15.6 [statistics.go]
編寫一個網頁程序,可以讓用戶輸入一連串的數字,然後將它們打印出來,計算出這些數字的均值和中值,就像下邊這張截圖一樣: